Anything that can be quickly liquidated into cash is considered cash. Cash activities are a large part of any business, and the flow of cash in and out of the company is reported on the statement of cash flows. It shows the effect of every transaction taking place and how it affects the corporation’s liabilities. Further, it also elaborates on the detailed aspects of any increase in cash flows on account of revenue earned or any decrease in cash flows on expenses incurred for running the operations. Unearned revenue represents a customer’sadvanced payment for a product or service that has yet to beprovided by the company. Since the company has not yet provided theproduct or service, it cannot recognize the customer’s payment asrevenue, according to the revenue recognition principle.
Learning Outcomes
- If a business has net loss for the period, this decreases retained earnings for the period.
- Well the expanding formula shows the relationship between the income statement and the balance sheet.
- Shaun Conrad is a Certified Public Accountant and CPA exam expert with a passion for teaching.
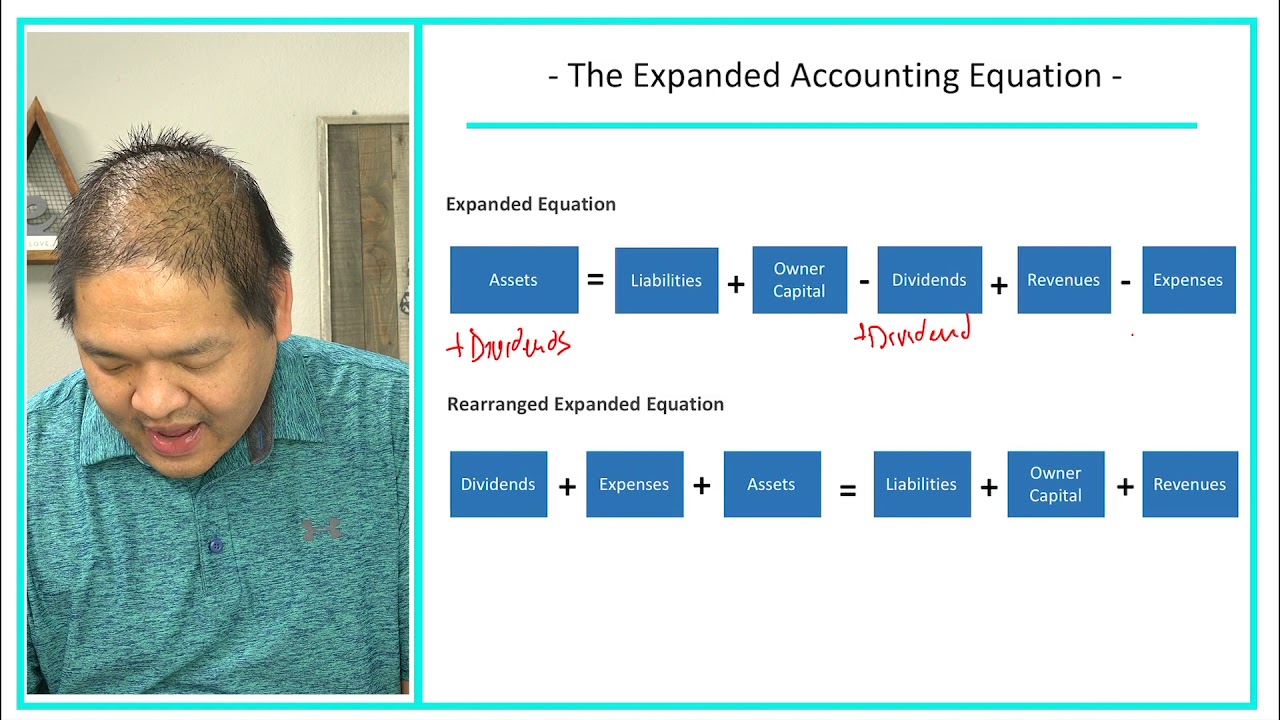
This expanded equation takes into consideration the components of Equity. Equity increases from revenues and owner investments (stock issuances) and decreases from expenses and dividends. These equity relationships are conveyed by expanding the accounting equation to include debits and credits in double-entry form. The assets in the standard accounting equation are the resources that a company has available for its use, such as cash, accounts receivable, fixed assets, and inventory.
Our mission is to improve educational access and learning for everyone.
By decomposing equity into component parts, analysts can get a better idea of how profits are being used—as dividends, reinvested into the company, or retained as cash. Expenses refer to the costs and expenses the company incurred to generate its revenues. The Basic Accounting Equation should typically be your go-to formula for broadly assessing your company’s finances. It indicates the net resources you have at your disposal for sustaining operational needs. Just like algebra enables you to break down complex math problems into manageable parts, understanding this equation can arm you with valuable knowledge for steering the financial strategy of your business.
What is the expanded accounting equation?
The first subcategory represents the owner’s stake in the business. The second shows how much money the owners capitalizing software development costs for saas companies took out of the company. The third and fourth items represent the income and expenses for the year.
Forexample, a company may have accounts such as cash, accountsreceivable, supplies, accounts payable, unearned revenues, commonstock, dividends, revenues, and expenses. Each company will make alist that works for its business type, and the transactions itexpects to engage in. The accounts may receive numbers using thesystem presented in Table 3.2.
To solve a balance sheet, record all transactions properly and calculate total assets, liabilities, and equity using respective formulae. Finally, verify that both sides of the equation, i.e., Assets and (Liabilities + Equity) are equal. As you dive deeper into understanding this equation, you will see a clear picture depicting how business operations affect company finances down to expenses and revenue levels.
Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.

Liabilities are obligations to pay an amount owed to a lender (creditor) based on a past transaction. It is important to understand that when we talk about liabilities, we are not just talking about loans. Money collected for gift cards, subscriptions, or as advance deposits from customers could also be liabilities. Essentially, anything a company owes and has yet to pay within a period is considered a liability, such as salaries, utilities, and taxes.

